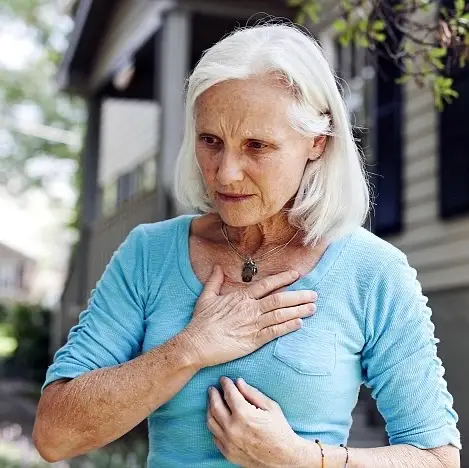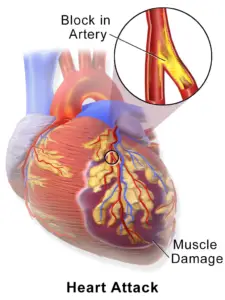
Heart attacks can be categorized based on whether an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) reveals specific changes (ST elevation) necessitating urgent invasive treatment. • An acute complete blockage of a medium or large coronary artery is typically diagnosed as an ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). • A partial blockage often corresponds to a non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), although some individuals with NSTEMI may have a total blockage.
It’s important to note that not all heart attacks are caused by blocked arteries. Other factors include:
• Coronary artery spasm, a severe constriction of a non-blocked blood vessel, which can occur in arteries with cholesterol plaques or early vessel hardening due to smoking or other risk factors. This condition may also be referred to as Prinzmetal’s angina, vasospastic angina, or variant angina.
• Certain infections, such as COVID-19 and other viral infections, may lead to heart muscle damage. • Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD), a life-threatening condition resulting from a tear within a coronary artery.
Heart Attack Risk Factors

1.
Age: Men over 45 and women over 55 face higher risk. 2. Tobacco use: Smoking and secondhand smoke exposure increase risk.
3. High blood pressure: Especially when combined with obesity, high cholesterol, or diabetes. 4.
High cholesterol or triglycerides:Elevated LDL and triglycerides, and low HDL increase risk. 5. Obesity: Linked to high blood pressure, diabetes, and unfavorable cholesterol levels.
6. Diabetes: High blood sugar raises heart attack risk. 7.
Metabolic syndrome: A combination of central obesity, high blood pressure, low good cholesterol, high triglycerides, and high blood sugar doubles the risk. 8. Family history: If a close relative had an early heart attack, your risk increases.
9. Lack of exercise: A sedentary lifestyle is associated with higher risk. 10.
Unhealthy diet: High sugar, animal fats, processed foods, trans fats, and salt intake raise risk. 11. Stress: Emotional stress, like extreme anger, can increase heart attack risk.
12. Illegal drug use: Cocaine and amphetamines can trigger heart attacks. 13.
Preeclampsia history: Increases the lifetime risk of heart disease. 14. Autoimmune conditions:Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can increase heart attack risk.